History
Timeline
Fifth generation (1991 - )
Japan announces its strategy for building sixth-generation, neural network-based computers
 Apple, IBM and Motorola start to develop the Power PC microprocessor family
Apple, IBM and Motorola start to develop the Power PC microprocessor family
Sun sells machines with RISC architecture and fine tunes the Solaris operating system
AMD introduces the 386 DX, the first Intel 386 clone, and breaks the Intel monopoly
Linus Torvalds programs Linux, a variant of the Minix operating system (created by Andrew S.Tannenbaum) in his spare time. The code of the new operating system was quickly distributed free of charge over the Internet
IRIS is renamed as RedIRIS, which is today’s national academic and research network
Languages for communicating with remote programs, such as CORBA, are released. CORBA was based on a joint proposal by
Dec, HP, NCR, and Sun
Sun sells the SPARCstation 10, its first desktop multiprocessor computer
The Michelangelo virus is distributed over the Internet, causing great concern among internauts

DEC introduces the first chip to implement Alpha, its 64-bit RISC architecture
Apple releases Newton, a PDA (personal digital assistant), which was to become very popular
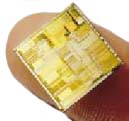
Intel introduces Pentium, a microprocessor with 3.1 million transistors and a speed of 60 MHz
The Cray T3D multicomputer is developed. Operating at speeds from 25 gigaflops to 1.5 teraflops, it was designed to solve problems requiring supercomputing in the fields of biology and chemistry
The National Center for Supercomputing Applications at the University of Illinois develops Mosaic, a graphical user interface for Web browsing
IBM launches ThinkPad 750. The first "notebook" to travel into space onboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour on a mission to repair the Hubble Space Telescope
Jim Clark and Marc Andreesen form the Netscape Communications company and release the first version of their browser
Leonard Adleman of the University of Southern California shows that DNA can be used as a means of computing
After three years of preliminary versions, version 1.0 of the Linux kernel is released
The feature film Toy Story is released. It was completely computer animated

Sun Microsystems Inc creates Java. This software can be used to develop platform-independent applications. Duke was the first applet
Borland introduces Delphi a programming environment for fast application development
DVD (Digital Versatile Disc) is released to meet needs for a common standard format for video, audio and data

Microsoft sells the first version of the Windows operating system: Windows 95. The launch was supported by a spectacular advertising campaign
Pentium Pro is announced. Pentium Pro contained 5.5 million transistors and ran at a speed of 150 MHz
There are an estimated 10 million Internet users worldwide
A consortium of several companies develops the CD-RW (Compact Disc-ReWritable)
Sun Ultra, a workstation with a 64-bit UltraSPARC processor with on-chip multimedia, is launched
Intel releases Pentium II. Pentium II contained 7.5 million transistors and ran at speeds of around 233 MHz
IBM Launches ASCI Deep Blue, a supercomputer capable of evaluating 20 million chess positions per second. The world champion Gary Kasparov can evaluate only 3 positions per second
Microsoft put up for sale Windows 98, Windows 95 review, which are fixed many bugs and added new features
Stanford University students Larry Page and Sergey Brin create the PageRank search engine to automatically track Internet addresses. This algorithm is the heart of Google
Intel’s Pentium III comes on the market. It contained 28 million transistors and ran at speeds of around 400 MHz
AMD releases the Athlon 2000 processor
The AMD Athlon is the first domestic processor to reach speeds of 1 GHz. It contained 37 million transistors
The inventors of the integrated circuit receive the Nobel Prize in Physics
Intel Pentium 4 is released. It was built with 48 million transistors and reached speeds of 1.5 GHz
IBM’s ASCI White supercomputer, capable of speeds around 12.3 teraflops, is released
The number of Internet users worldwide reaches about 500 million people, Some 120 million are in Europe and 7 million are Spanish
El número de usuarios de alguno de los servicios de Internet es de casi 500 millones de personas en todo el mundo, de las que 120 millones son europeas y más de 7 millones españolas
